What are the knowledge base settings?
Every knowledge base has a settings modal. This modal is shared by Documents + Search, URLs + Search, Google Drive, Notion, Data + Search and Azure Blob, which can be accessed by clicking on the settings icon, allows you to configure How did your knowledge base handle the embeddings and the chunks that were extracted from your data sources?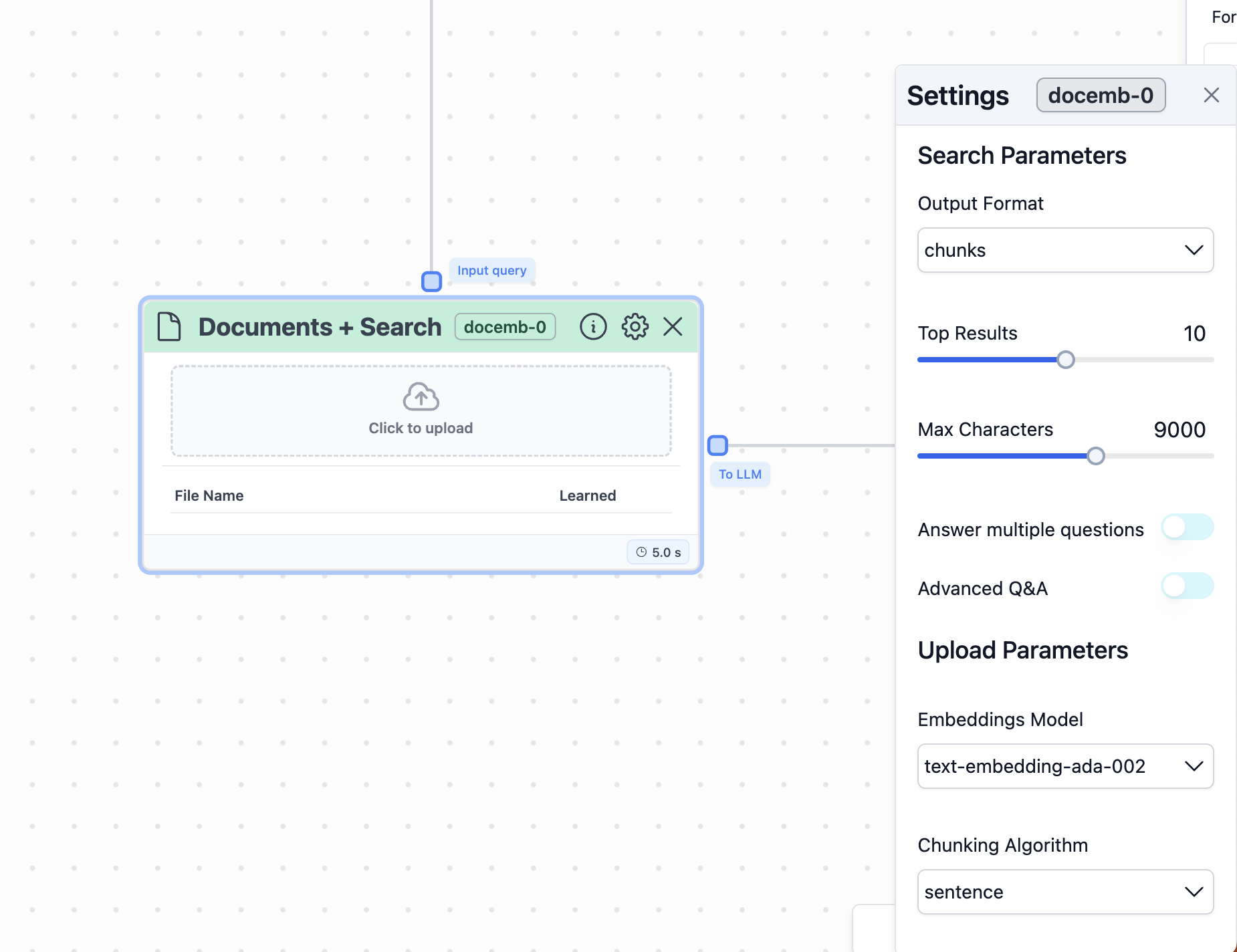
Settings in a Documents + Search node
Upload parameters section in settings
The first section in the settings modal is theUpload parameters section.
Here, you will find the parameters related to the knowledge base search.
The parameters are the following ones:
Retrieval algorithm: the system uses chunks by default. You can also choose
docs or pages: - chunks will return the most relevant chunks of the various
documents in your knowledge base. The size of each chunk can be configured in the
chunk length parameter. - pages will return the most relevant pages (i.e., entire
pages) from the documents in your knowledge base. - docs will return the most relevant
documents (i.e., entire documents) in your knowledge base.
Top results: By default, the system uses the top 10 results
from the query (greatest similarity with regards to your input query). You can also
choose as many as you want by clicking the number and editing it.
Result length: This parameter corresponds to the character length
of the text returned from the node. By default, the system uses 5000.
You can also select as many characters as you want by using the sliding bar, clicking
the number, and editing it. Please be careful about the context window of your LLM. If you send
to many characters, there might be an error.
Advanced Q&A: By enabling this feature, the knowledge base search
will automatically use ```retrieval utilities“ to select the best mechanism to answer
the user questions depending on whether the question aims to:
- Retrieve a fact.
- Compare a set of documents.
- Summarize a document inside the knowledge base.
Upload parameters section in settings
The second section in the settings modal is theUpload parameters section.
This section allows you to configure how your knowledge base handles the embeddings
and the chunks that are extracted from your data sources.
The parameters in this section are:
-
Select the model for embeddings: You can select the AI model
used to generate the embeddings. As default, the
text-embedding-ada-002 modelfrom OpenAI is selected. The alternative option is theazure-text-embedding-ada-002 model. -
Chunking algorithm: by default, the system uses
sentence. You can also choosenaive. -
Chunk overlap: This is the amount of overlap between chunks.
This is often helpful to make sure that the text isn’t split weirdly. By default,
the system uses
500. You can also choose as many as you want by clicking the number and editing it. -
Chunk length: This is the amount of characters of each chunk
returned. It is important to have a balance between preserving context and maintaining
accuracy. Start by exploring a variety of chunk sizes, including smaller chunks
(e.g., 100-500 tokens) for capturing more granular semantic information and larger
chunks (e.g., 1000 or 2000 tokens) for retaining more context. By default, the
system uses
1500. You can also choose the length that you want by using the sliding bar or clicking the number and editing it. - Advanced Data Extraction: Enable it if you want to extract text from images that are present in your documents. By default, this option is deselected since it will increase the latency of your workflow (i.e., it will run slower).
- Embeddings API key: by default, the text field is empty. Stack AI’s API key are used. If you would like to use yours, then include your API key in this text field.
More information on chunking algorithms
Please find below a description ofsentence and naive chunking algorithms and the difference between the two:
Naive Algorithms - Simplicity: naive
algorithms are typically simpler and less sophisticated. They often rely on
basic methods like searching for specific keywords or phrases. -
Lack of Context Understanding:
they usually don’t understand the context or the structure of the
language. For example, a naive algorithm might count the frequency of words
without understanding their meaning or part of speech. -
Speed and Efficiency:
due to their simplicity, these algorithms can be faster and more
efficient, especially for straightforward tasks. -
Limitations:
naive algorithms are generally less accurate in complex language
processing tasks. They might miss nuances, sarcasm, or idiomatic expressions.
Sentence Chunking Algorithms -
Complexity:
these algorithms are more sophisticated. They involve breaking down
text into syntactically correlated parts of words like noun phrases, verb
phrases, etc. - Context and Structure Understanding: sentence
chunking algorithms understand the structure of a sentence. They analyze parts
of speech and how words relate to each other in a sentence. -
Accuracy:
they are more accurate in understanding the meaning and context of
sentences. This makes them suitable for complex tasks like sentiment analysis,
information extraction, and language translation. -
Resource Intensity:
these algorithms are usually more resource-intensive due to their
complexity. They might require more computational power and time to process
text.
